DL1 : Deep Learning Algorithms ~ Analyzing Neural Networks
- 3 mins
Although deep neural networks have brought promising results to key areas such as computer vision, speech recognition and language understanding, it remains a challenge to understand the workings of these networks beneath the hood. I will attempt to firstly go through the basic idea in building a neural network and subsequently explain how the scalable programming framework Tensorflow eases the creation of deep learning models through numerical computation using data flow graphs.
Deep learning represents state of the art approaches for predictive modelling in today’s data driven society. They are however limited by memory constraints on hardwre devices used for training. Generally, there are multiple variants of a neural network model and they each have their specific use.
1) ANN
2) RNN- recurrent networks for sequence generation
3) CNN- convolutional networks for image recognition/ classification
4) GAN- generative adversarial networks for image generation
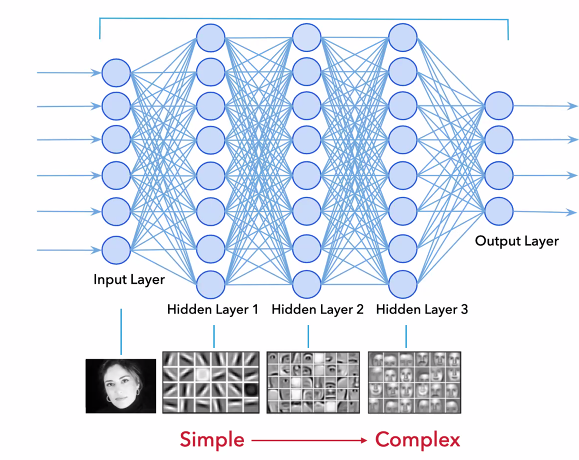
The simplest is a feed forward neural network, where the idea is to stack multiple models to discover hidden patterns.The network is represented as a nested matrix as seen in the image below. Each neuron receives some inputs (vectors) and is transformed through a series of hidden layers, with the last layer being being the output layer:
Reccurent neural networks, a class of deep learning algorithms, were first designed to help predict sequences. They broadly fall into 2 categories, LSTM and Gated RNN and they work on data sequences of the variable input length. It puts the knowledge gained from the previous state as an input value for the current prediction. This is because the neurons send feedback signals to each other through hidden states. This architecture enables them to keep prior inputs in memory while predicting the current input and output, unlike feed forward neural networks. While it has been used in time series model such as the management of stock price changes, it is a technique that can also be used to predict consumer behaviour from their interaction history. Consumer history can be viewed as a sequence of events. It captures and holds important important clues that can be used for predictions. For example, we may want to find out the propensity of a customer to order within the next 7 days, from the time they engaged and viewed the product.
In CNN, the explicit assumption here is that the input are images and the algorithm learns through data compression and image denoising.
Broadly speaking, there are 3 important components in building a neural network:
1) Activation function - examples are sigmoid, tanh, Rectified Linear unit(relu). Softmax function normalizes arbitary values using exponential distribution and it is used for multilabel classes where the sum of the outputs is not necessarily 1
2) Loss Function - which is the proxy to obtaining the ideal parameters. Example is binary cross entropy for multi-class classification problem.
3) optimizer - finiding the optimal weights to the problem on hand. Examples are SGD, momentum, adam
Illustration of softmax :
Variational autoencoding is a probabilistic technique that is used to debias neural networks by probabilistically sampling the latent feature space.
Traditionally, feature engineering was applied on sequential data through machine learning models. In feature engineering, a vector of features are constructed from a given consumer history and this is provided as an input to a vector based machine learning model. Deciding on the exact choice of feature representation has decisive effects on a model’s performance and it is a tedious and laborious work, so an alternative to circumvent this is to look towards recurrent neural networks as they work directly on sequences as inputs.